Abstract
Background:
A number of international randomized clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of rituximab when added to existing chemotherapy regimens such as CHOP for the first line treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL) without inducing significant toxicity. Base on the published clinical evidences, rituximab-based regimen (R-chemo) was recommended for treating FL patients in China. Due to the low incidence of FL in China, the knowledge on safety and effectiveness of R-chemo in Chinese patients is scarce.
Methods:
This open-label, single-arm, multicenter, non-interventional study (NCT01340443) was designed to assess the safety and effectiveness of R-chemo in Chinese patients with FL. FL patients who were eligible to receive R-chemo (CHOP or non-CHOP) as first-line treatment were enrolled with no specific exclusion criteria. Individual dose and duration of treatment was determined at the investigator's discretion, local labeling information and standard clinical practice. Patients went through safety and efficacy assessment after the last rituximab dose was administered, and then followed-up for 3 years. The primary endpoints included adverse events (AEs), severe adverse events (SAEs), adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and adverse events of special interest (AESIs). Data for analyses were collected from medical records. This study was registered in clincialtrials.gov (NCT01340443).
Results:
A total number of 31 patients were enrolled by 12 sites. Twenty-three patients completed the study procedures. Twenty-nine patients received at least one cycle of rituximab and completed at least one tumor assessment after baseline, and they were included in the effectiveness analysis. The average age of these FL patients was 53.3 (12.25) years old. 72.4% of them were below 60 years old.
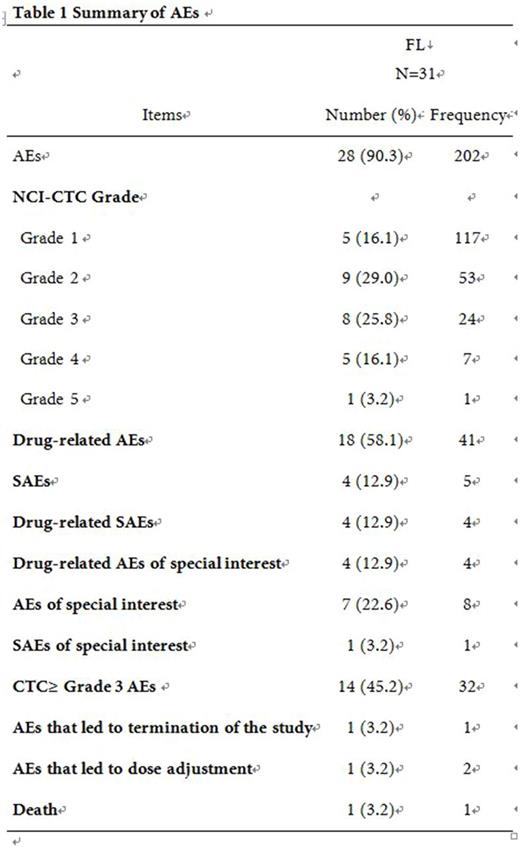
Safety analysis was performed in 31enrolled patients as they received at least one dose of rituximab. Twenty-eight (90.3%) FL patients reported 202 AEs (table 1). The shortest median duration was 1 day, reported from infusion related reaction. Sinus bradycardia associated with the longest median duration, which was 1446.0 days. Forty-one AEs in 18 (58.1%) FL patients were reported as drug (rituximab) related AEs. The most common drug-related AEs which had CTC ≥ 3 were bone marrow failure (6.5%), agranulocytosis (3.2%), lung infection (3.2%), upper respiratory tract infection (3.2%), white blood cell count decreased (3.2%), neutrophil count decreased (3.2%), and enteritis (3.2%). Drug-related AEs of special interest were infusion related reactions (6.5%) and other opportunistic infections (6.5%). Four (12.9%) FL patients reported 5 SAEs, while 4 cases were drug-related SAEs. The AE which led to death in FL patient was intestinal perforation (1 case) and was not related to observational drug. In term of effectiveness, final analysis showed that 2-year progression-free survival rate was 61% and the 2-year overall survival rate was 97%.
Summary:
This study further validated the safety and effectiveness of R-chemo in Chinese FL patients in real-life clinical practice. Safety profile of R-chemo was acceptable when it was used as first-line treatment. Good effectiveness was also achieved, although the patient number was limited.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal